Why AI Animation Errors Happen
AI animation tools are powerful but often produce errors that disrupt workflows and final results. Common issues include identity drift (characters changing appearance), temporal flicker (shimmering backgrounds), and motion incoherence (jerky or unnatural movements). These problems stem from how AI generates videos frame-by-frame without memory, poor prompt clarity, and the limitations of AI models in simulating physics or maintaining consistency.
Key Takeaways:
- Frequent Errors: Identity drift, motion incoherence, temporal flicker, and stagnation.
- Causes: Vague prompts, lack of scene memory, and frame-by-frame generation.
- Fixes: Use specific prompts, shorter clips (3–6 seconds), and tools like LongStories.ai for character consistency.
- Human Oversight: Frame-by-frame reviews and manual edits for critical elements are essential.
To minimize errors, focus on detailed prompts, choose the right tools, and maintain thorough human oversight during production. These steps can save time and improve animation quality.
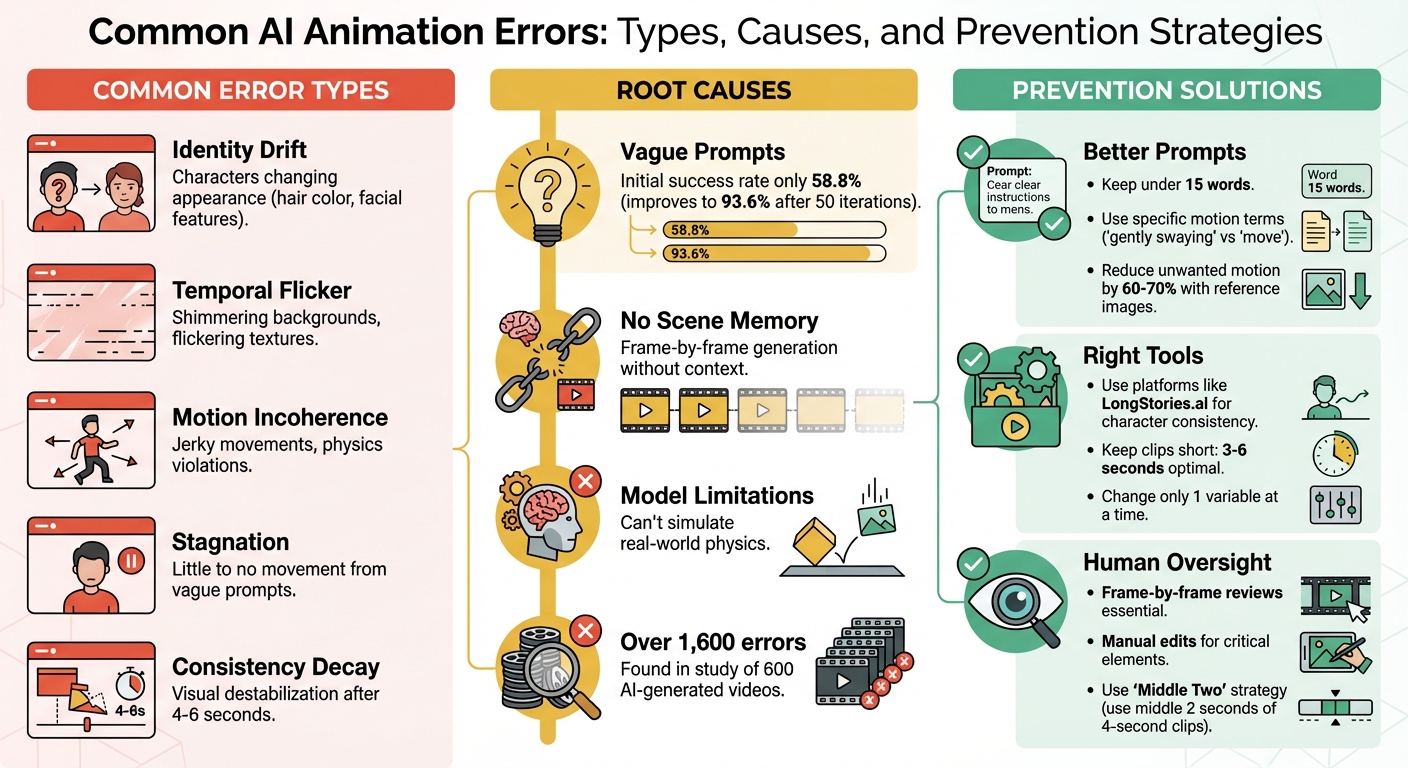
Common AI Animation Errors: Types, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
Why Most AI Films Fall Apart - And How to Fix It
Common AI Animation Errors
AI animation tools, while impressive, often come with their own set of quirks. Understanding these common errors can save you time and frustration by helping you identify and address issues early in the process.
Visual Artifacts and Distortions
One of the most noticeable issues is temporal flicker, where consecutive frames don’t align properly. This misalignment can create shimmering backgrounds or flickering textures. The root cause? Many AI models generate each frame independently, lacking a consistent visual memory to tie them together.
Another common problem is identity drift, where characters or objects subtly change over time. For instance, a character’s hair might shift from brown to blonde, or their facial features may gradually alter. These changes often go unnoticed during playback but become glaringly obvious when reviewing the video frame-by-frame.
AI models also struggle with consistency decay beyond 4 to 6 seconds of footage. This is when visual elements start to destabilize, particularly with complex features like faces and hands. The result? What creators often call "AI slop" - motion that feels floaty, shadows that don’t match the lighting, and an overall lack of emotional depth. To catch these errors, it’s helpful to examine the final few seconds of your video closely, looking for vanishing objects, mismatched shadows, or distorted character details.
Motion Quality Problems
Motion errors are another frequent challenge. Movements can appear jerky, twitchy, or disjointed, giving the impression of an animation cobbled together frame-by-frame instead of flowing naturally .
A specific issue, motion incoherence, occurs when actions don’t follow a logical path. For example, a character might walk smoothly, only to suddenly teleport forward, or an object might rotate in a way that defies basic physics. In one study of 600 AI-generated videos, researchers found over 1,600 detailed errors, with physics violations being a recurring problem.
Another issue, stagnation, arises when prompts for movement yield little to no change. Vague instructions like "a person moves" often fail to produce dynamic results. In contrast, more specific prompts, such as "a person walks forward with steady footsteps", tend to perform better.
The initial success rate for generating accurate motion can be as low as 58.8%. While iterative refinements can improve this to 93.6% within 50 attempts, each regeneration carries the risk of introducing new errors or worsening existing ones .
Temporal Consistency Problems
Without a global memory, even short-term details can drift. This leads to issues like characters flickering between slightly different versions of themselves, backgrounds shifting unexpectedly, or objects changing size or position without any logical reason .
Structural distortions and gradual attribute drift often stem from random diffusion noise and cumulative exposure bias . Tools like LPIPS (Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity) can help detect these inconsistencies by measuring visual differences between frames. Pay close attention to subtle issues like "mouth drift", where a character’s mouth changes expression unexpectedly, or camera instability, where the viewpoint shifts erratically.
What Causes AI Animation Errors
Understanding where AI animation errors come from can help address and prevent them. These errors typically stem from three main sources: unclear prompts, the limitations of the AI model itself, and challenges in integrating AI into existing workflows.
Prompt Complexity and Ambiguity
Unclear or contradictory prompts can confuse AI systems, leading to erratic or minimal motion. For example, asking for both "static" and "violent shaking" in the same prompt may result in unpredictable outcomes. Even a simple command like "make a person move" might generate only slight or awkward motion.
A 2025 study revealed that AI-generated motion graphics met prompt requirements just 58.8% of the time on the first try but improved to 93.6% after 50 iterations. However, each regeneration introduces the risk of new errors. The phrasing of prompts also plays a big role. Commands like "running at 20 mph" can trigger glitches, while descriptions such as "smooth charge forward" tend to produce more stable results.
Next, the inherent limitations of AI models can exacerbate these issues.
Model Limitations and Compatibility
Unlike traditional animation tools, AI models lack "scene memory", which leads to inconsistent movements. These systems predict motion based on training data but don't understand real-world physics. This is why you might see jerky motions or physically impossible actions - the AI is essentially guessing the next step based on patterns it has learned.
The capabilities of different engines also vary. Lower-tier engines, like "Turbo", often fail to maintain details such as mouth positions or consistent hairstyles. In contrast, advanced engines like Digen 2.6 Pro use specialized algorithms for smoother character animations. However, this comes with trade-offs. Techniques like smoothing can reduce flickering but may also blur fine textures and artistic details.
AI models also struggle when handling multiple subjects. For instance, faces can distort, characters may swap identities mid-motion, or the system may lose track of who’s interacting with whom. Standard video models like Sora or Kling are optimized for natural footage, not the exaggerated movements and stylized visuals common in animation.
Finally, integrating AI into established workflows introduces its own set of challenges.
Workflow Integration Problems
Integrating AI into traditional workflows can create significant disruptions. Many AI systems operate as "black boxes", meaning their decision-making processes are opaque. This lack of transparency makes troubleshooting nearly impossible.
"Our animation teams require transparency in their tools to maintain creative oversight. When AI systems can't explain their decision-making process, artists lose confidence in the technology." - Michelle Connolly, Founder, Educational Voice
Traditional animation workflows allow precise adjustments, such as tweaking Bézier curves or keyframes. In contrast, AI workflows rely on probabilistic outputs - changing a prompt regenerates the entire animation instead of refining specific elements. This trial-and-error approach wastes time and often introduces inconsistencies. Solving these integration challenges is critical for maintaining efficiency and avoiding compounded errors across iterations.
sbb-itb-94859ad
How to Prevent AI Animation Errors
Avoiding AI animation errors requires a mix of better workflows, smarter tool choices, and careful human oversight.
Writing Better Prompts
The structure of your prompts plays a huge role in the quality of the output. Start by using a high-quality static reference image for image-to-video tasks. This gives the AI a clear "ground truth" for elements like lighting and environment, reducing unwanted motion by 60-70%.
Keep prompts concise - stick to 15 words or fewer - to focus on the primary action. Place essential instructions at the beginning, and use delimiters like ### or """ to separate context from commands.
Be specific about what moves and what stays still. For example, terms like "Static camera", "Locked-off shot", or "Tripod mounted" can prevent unwanted camera drift. Instead of vague directives like "make a person move", use precise language such as "gently swaying", "smoothly rotating", or "flowing" to guide the motion.
For character consistency, reiterate defining features - things like hair color, eye color, skin tone, and outfit - in every prompt. This prevents characters from morphing between scenes. A smart approach is to create a base prompt template that locks in these fixed attributes while allowing you to adjust only the background or action for new scenes. This method helps tackle issues like identity drift and temporal inconsistencies.
"The granularity of your input is directly proportional to the utility of the output you receive." - MIT Sloan Teaching & Learning Technologies
Another tip: use the "Middle Two" strategy. Generate a 4-second clip, but only use the middle 2 seconds in your final edit. This avoids the jitter at the start and the drift that often happens near the end of AI-generated sequences.
Using the Right Tools and Platforms
Once your prompts are fine-tuned, choosing the right tools becomes critical. The platform you select can significantly influence error rates. For example, LongStories.ai offers "Universes" that store character, style, and voice data, eliminating the need for repetitive prompting and reducing identity drift in long-form content. The setup takes just 3 to 15 minutes and allows for unlimited consistent video generation. Additionally, creating a comprehensive asset pack - like a Character Master, Expression Set, and Pose Set - can ensure consistency across projects.
"We were working with a team to create shots for our YouTube series, and we couldn't work on more than 1 episode per week. Now we can make several a day." - Film Studio using LongStories
For better results, change only one variable at a time. Keep outfits and environments locked while focusing on altering just the action or emotion in a shot. Use animatics as a cost-effective way to identify pacing or shot errors before diving into full production. Instead of generating dozens of variants, try the "Shot Factory Loop": produce 2–6 variants, select the best one, and refine it with masking or inpainting.
Keeping Human Oversight in the Process
Even with optimized prompts and advanced tools, human oversight remains essential. AI enhances workflows but doesn’t replace human judgment. A frame-by-frame review is key to spotting subtle issues like flickering objects, morphing details, or inconsistent shadows that automation might overlook.
"The animatic is your cost filter. When you watch your story play out with timing and rough audio, you immediately discover pacing problems, missing shots, and shots that don't communicate the beat." - Sachin Kamath, Co-founder & CEO at Neolemon
Iterative review loops can dramatically improve results. Human editors should handle "hero" elements - such as characters, logos, or key actions - using traditional tools like After Effects or puppet rigging. Meanwhile, AI can take care of backgrounds and mood shots. Keep shots short (3–6 seconds) and manually stitch them together to minimize visual degradation. Finally, use shot spec cards for every shot. These cards should include reference images, detailed prompts, and continuity notes to ensure the AI stays aligned with your creative vision.
Conclusion
AI animation errors often arise from challenges in identity, motion, and temporal coherence. These issues are frequently triggered by vague prompts or by attempting to generate clips longer than 3–6 seconds.
To address these challenges, focus on structured prompts that lock in character details and camera angles. Stick to shorter clip durations to ensure smoother stitching and consider creating asset packs to maintain character consistency across scenes. At its core, avoiding these errors boils down to three essentials: precise inputs, the right tools, and thorough reviews.
Platforms like LongStories.ai simplify this process by allowing users to store characters, styles, and voices in reusable "Universes." This reduces the need for repetitive prompting and helps prevent identity drift in long-form content. By integrating automated tools with careful human oversight, creators can strike the right balance to minimize errors.
"The motion designers who'll thrive are the ones who... combine AI's creative freedom with human discipline." – AI.in.motion
This quote highlights the importance of blending AI's potential with human precision. To achieve this, conduct frame-by-frame reviews to catch subtle issues like flickering or unrealistic physics. Use AI for tasks like generating backgrounds or setting the mood, but rely on manual tools like After Effects for critical elements such as logos, main characters, and key actions. The aim is not to replace human judgment but to enhance creativity through disciplined refinement.
FAQs
How can I keep characters consistent in AI animations?
To keep character consistency in AI animations, it's essential to use reference frames or anchors at various points in the animation. These act as guides, ensuring the character's appearance and movements stay aligned throughout the process. Alongside this, maintaining detailed documentation and building reference libraries for your characters - covering their design, movements, and overall style - can help avoid inconsistencies or "identity drift."
You can also streamline consistency by using platforms that offer reusable assets, such as pre-set character templates or "Universes." These tools are especially useful for maintaining a unified style across multiple projects while saving time. For creators aiming to scale their work without compromising quality, such resources can be a game changer.
How can I keep my AI-generated videos consistent in style and quality?
Consistency is key when crafting AI-generated videos that reflect a polished and unified brand image. Tools like LongStories.ai make this process easier by offering reusable "Universes." These templates let you lock in consistent characters, styles, and voices, so you don’t have to tweak settings repeatedly. The result? Every video seamlessly aligns with your brand’s identity.
To further streamline your workflow, consider using reference images, building detailed character profiles, and fine-tuning AI models to match specific visual or stylistic preferences. These steps not only save time but also ensure your videos maintain a professional, cohesive appearance across all your projects.
Why is human involvement essential in AI animation production?
Human input plays a key role in AI animation production, especially when it comes to addressing challenges like identity drift, scene inconsistencies, and motion instability. These issues often stem from the way AI models handle animations - processing them one frame at a time - which can cause small deviations to build up, particularly in lengthy or intricate scenes.
With human oversight, creators can ensure visual consistency and maintain the quality of storytelling, avoiding distractions that might pull viewers out of the experience. Blending the speed of AI with the precision of human review leads to refined, professional animations that stay true to the intended creative vision.
Related posts
LongStories is constantly evolving as it finds its product-market fit. Features, pricing, and offerings are continuously being refined and updated. The information in this blog post reflects our understanding at the time of writing. Please always check LongStories.ai for the latest information about our products, features, and pricing, or contact us directly for the most current details.