
Study: AI in Multilingual Storytelling
AI is transforming how children learn languages and understand diverse perspectives through personalized multilingual storytelling. By tailoring stories to each child's language skills and interests, these tools support language development, cognitive growth, and cultural awareness. With 5.3 million multilingual learners in U.S. classrooms, AI storytelling platforms address the growing need for engaging, individualized learning experiences.
Key Highlights:
- AI uses machine learning and natural language processing to create personalized, real-time stories in various languages.
- Benefits include improved vocabulary, problem-solving skills, and empathy, especially for multilingual learners.
- Interactive features like voice narration, visuals, and feedback make learning more engaging than traditional methods.
- Tools like LongStories.ai generate tailored, animated stories in under a minute, providing accessible educational content.
- Challenges remain in supporting underrepresented languages and ensuring ethical, culturally sensitive AI development.
AI storytelling offers scalable solutions to bridge language gaps while celebrating diversity, making it a valuable tool for educators and families.
AI for Multilingual Learners - Why and How (CDE)
Research on AI and Children's Language Development
Studies reveal that AI-powered storytelling can significantly enhance children's language and cognitive skills. These interactive platforms show measurable improvements in vocabulary, comprehension, and effective language use across various languages.
Unlike traditional books, AI-driven systems adapt in real time to a child's learning pace and interests, creating personalized pathways for language development. This real-time adjustment plays a key role, particularly in expanding vocabulary.
AI and Vocabulary Growth
AI storytelling tools are transforming how children learn vocabulary, comprehension, and narrative skills through interactivity and personalization. Using voice recognition and adaptive algorithms, these platforms deliver immediate feedback and adjust content to match each learner's abilities. By incorporating audio, visuals, and interactive challenges, these tools go beyond what conventional methods can achieve. They even analyze user behavior to fine-tune word difficulty, pace, and review timing, employing spaced repetition techniques to support long-term retention.
Ying Xu, an Assistant Professor at the Harvard Graduate School of Education, highlights the potential of interactive AI storytelling. She notes:
"So what we've found is that children who engage in this type of interactive dialogue with AI comprehend the stories better and learn more vocabulary, compared to those who just listen to the stories passively. And in some cases, the learning gains from interacting with AI were even comparable to those from human interactions."
Data further underscores these benefits: children read to daily are six times more likely to exceed their age-level reading skills than those who aren't. AI tools make vocabulary learning more engaging by integrating features like audio pronunciation, visuals, usage examples, and interactive challenges. They also suggest related words, encouraging natural vocabulary expansion.
Beyond just vocabulary, AI-generated narratives spark deeper cognitive engagement.
Building Awareness Through AI-Generated Stories
AI-generated stories do more than teach language; they encourage broader cognitive development. Tailored narratives based on a child's interests not only boost engagement but also promote sustained reading habits. These interactive stories allow children to shape the plot, fostering creativity, imagination, and problem-solving skills.
Research also highlights the cognitive advantages of multilingualism, which include improved executive function, metalinguistic awareness, and problem-solving abilities. Brain imaging studies reveal that multilingual children have stronger neural connections, enabling more efficient information processing. Additionally, multilingualism has been linked to delaying age-related cognitive decline by up to five years. While this research primarily focuses on adults, it suggests that early multilingual exposure through AI storytelling could provide lifelong cognitive benefits.
Addressing Low-Resource Languages
Ensuring that AI supports underrepresented languages is vital for equitable education worldwide. Despite its promise, current AI models - especially large language models (LLMs) - often struggle with low-resource languages due to limited training data. Of the approximately 7,000 languages spoken globally, fewer than 5% have a meaningful online presence. This digital divide excludes many communities from accessing the educational and economic opportunities AI tools can offer.
The disparity is striking. While LLMs excel for widely spoken languages like English, they falter for languages like Vietnamese, spoken by 97 million people, or Nahuatl, an indigenous language. Even Swahili, spoken by around 200 million people, faces challenges due to a lack of digitized resources for AI training.
Sanmi Koyejo, an Assistant Professor at Stanford School of Engineering, emphasizes the consequences:
"If language technology does not work effectively for people in their native language, those communities miss out on the technology's benefits."
To address these gaps, researchers are exploring various approaches, such as training large multilingual models, developing smaller language-specific models, and creating regional models. Each method comes with trade-offs in performance, cost, and cultural representation. Automatic translation can help bridge data gaps, but it often fails to capture the nuances and context crucial for storytelling.
Beyond technical hurdles, ethical concerns arise around data collection and cultural representation. Gathering data from underrepresented communities risks exploitation if not handled with care. Despite these challenges, progress is being made. Some AI storytelling platforms now support 11 languages, including English, French, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Russian, German, Korean, Hebrew, Azerbaijani, and Arabic. However, this still represents only a small fraction of global linguistic diversity.
Looking ahead, success will require investments in research and development for low-resource language AI, efforts to promote inclusivity in AI research, and frameworks ensuring equitable data ownership. Additionally, performance evaluations must move beyond English-centric standards to truly support diverse linguistic communities.
AI Approaches to Multilingual and Relevant Storytelling
When creating AI storytelling systems for diverse languages, developers face a delicate balancing act: blending technical capabilities with an understanding of cultural authenticity. This balance is essential for addressing the challenges of both technology and culture in AI-driven storytelling.
Multilingual Models and Their Trade-Offs
Developers working on multilingual storytelling systems must navigate a range of architectural choices, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Large multilingual models, for example, can handle many languages but often struggle with cultural nuances and specific terminology. On the other hand, language-specific models dive deeper into cultural contexts but require significantly more resources to develop.
The scope of these challenges becomes apparent in real-world examples. In July 2025, Appen collaborated with a global tech company to improve a large language model across 30 languages and more than 70 dialects. This effort involved native speakers evaluating over 250,000 dialogue interactions to ensure the model delivered coherent, fluent, and culturally relevant results. Initially supporting just 10 dialects across 5 languages, the model's capabilities expanded significantly through this rigorous process.
Even with such advancements, limitations persist. Research shows that up to 47% of contextual meaning can be lost in traditional machine translation systems. To address this, multi-agent AI frameworks are gaining traction. These frameworks use specialized components to tackle various aspects of translation and cultural adaptation.
Here’s how these frameworks work:
- Translation Agent: Ensures grammatical accuracy.
- Interpretation Agent: Adds cultural and historical context.
- Content Synthesis Agent: Structures the final output while maintaining idiomatic expressions.
- Quality and Bias Evaluation Agent: Cross-checks historical data and identifies potential biases.
This multi-agent approach produces translations that feel more natural and culturally aligned. AI systems equipped with these capabilities achieve a 78% success rate in capturing cultural nuances, compared to just 45% for traditional methods. Additionally, automated cultural adaptation has cut the time needed for market-specific modifications by 73%, all while maintaining high accuracy.
Olga Beregovaya, Vice President of AI at Smartling, highlights a key challenge:
"There is this huge thing with most of these models still being English-language and English-phenomena centric."
This English-centric bias often leads to translations that, while technically correct, fail to capture the cultural subtleties critical for compelling storytelling.
Ensuring Sensitivity in AI Models
Beyond technical considerations, cultural sensitivity plays a vital role in AI storytelling. For educational applications, culturally aware adjustments not only enhance engagement but also improve learning outcomes. Achieving this requires a deep understanding of social norms and a commitment to avoiding stereotypes, while authentically representing diverse perspectives. Diverse training data is essential for equipping AI with the linguistic patterns, social norms, and cultural nuances needed to create meaningful content. This is particularly relevant given findings that Black adults spend 21% more time engaging with media than the average adult, highlighting the demand for culturally resonant material.
Human oversight is a critical safeguard. Experts emphasize the importance of using unbiased, diverse datasets and integrating human intervention during development to address potential biases. Adaptive learning mechanisms also allow AI models to evolve based on user feedback and real-world interactions. Designing systems with inclusivity in mind - by actively seeking out alternative voices and examples - broadens the cultural reach of AI-generated content. Involving linguists, cultural experts, and native speakers throughout the development process ensures the final output aligns with the intended cultural context.
Real-world applications showcase both the potential and challenges of culturally sensitive AI. In Rwanda, a multilingual AI system is helping community health workers communicate across language barriers. Using OpenAI's ChatGPT 4.0, trials achieved 71% accuracy in patient interactions, enabling more people to receive timely care. Crystal Rugege, Managing Director of the Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Rwanda, elaborates:
"We built a translation model that's both voice- and text-based, so they can interact with it and be able to discern if someone has a headache; if someone has a cough."
This example demonstrates how culturally aware AI can bridge communication gaps and address local needs - principles that are just as critical for educational storytelling.
sbb-itb-94859ad
AI Scalability and Accessibility in Educational Storytelling
AI-powered multilingual storytelling holds the potential to reach every child, regardless of their language or economic background. As schools around the world face increasing diversity and limited resources, scalable AI solutions present a chance to make personalized learning accessible to all. This section explores efforts to improve language representation and broaden access to AI in education.
Expanding Representation for Underrepresented Languages
A lack of digital support for many languages creates barriers for millions of children. Out of the roughly 7,000 languages spoken worldwide, only 50 to 100 are supported by major operating systems and browsers. This gap is particularly alarming given demographic trends: by 2050, over one-third of the world's youth will live in Africa, yet none of the top 34 languages on the internet are African.
AI chatbots, typically trained on about 100 languages, leave large populations without access to educational tools in their native tongues. Initiatives like Stanford's SILICON project aim to address this by bringing together language communities, tech leaders, international organizations, and academic institutions to promote digital inclusion.
Meta, for example, is collaborating with the Indian government to ensure its open-source large language model supports all 22 of India’s official languages. As Yann LeCun, Meta's Vice President and Chief AI Scientist, puts it:
"What we need is a very simple open infrastructure – think of it as a 'Wikipedia for AI' – so you give people the ability to build the systems that are useful for local populations."
The City of Boston demonstrates how AI can enhance accessibility. By integrating generative AI into its 311 system, the city now supports communication in 14 languages, improving citizen engagement.
Making AI Educational Tools Accessible to All
Representation is only part of the equation - ensuring that AI tools are accessible is equally important. The global AI in education market, valued at $1.82 billion in 2021, is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 36.0% through 2030. Affordable AI tools, some costing as little as $25 per month, are helping budget-conscious schools adopt personalized learning solutions.
One rural school in Kenya showcased the transformative power of AI. By integrating AI-supported emoji tools into the curriculum, the school saw test scores jump from 58% to 79% and retention rates improve from 70% to 88% in just six months. Teachers noted increased student engagement and better understanding of complex topics, particularly in multilingual classrooms.
AI systems adapt learning materials to each student’s skill level and pace, a feature especially beneficial in resource-limited settings where one-size-fits-all methods often fail. Additionally, AI tools can automate grading for assignments, quizzes, and exams, freeing up educators to focus on teaching.
Platforms like LongStories.ai highlight how AI can transform educational storytelling. This platform generates fully voiced, animated cartoons from a single text prompt in under a minute, removing barriers like high costs and technical complexity. Since its launch, it has produced over 5,000 video adventures, turning passive screen time into active learning.
Meghan Maneval, a leader in responsible technology, underscores the importance of inclusivity:
"Inclusive AI is not a luxury - it's a necessity. If our systems aren't built for everyone, they're not secure for anyone. Implementing AI responsibly is making it equitable and fair."
To ensure true accessibility, AI systems must be designed with diverse needs in mind. This includes using readable fonts, non-triggering color schemes, and intuitive workflows. Training datasets should reflect global diversity to minimize errors. Partnerships with tech companies and governments can also help provide essential resources, such as affordable internet plans and devices, to underserved communities.
Investing in open-source AI solutions and fostering collaborative partnerships will be key to making personalized, culturally relevant storytelling a universal educational tool rather than a privilege for a select few.
Case Study: LongStories.ai and Personalized Multilingual Storytelling
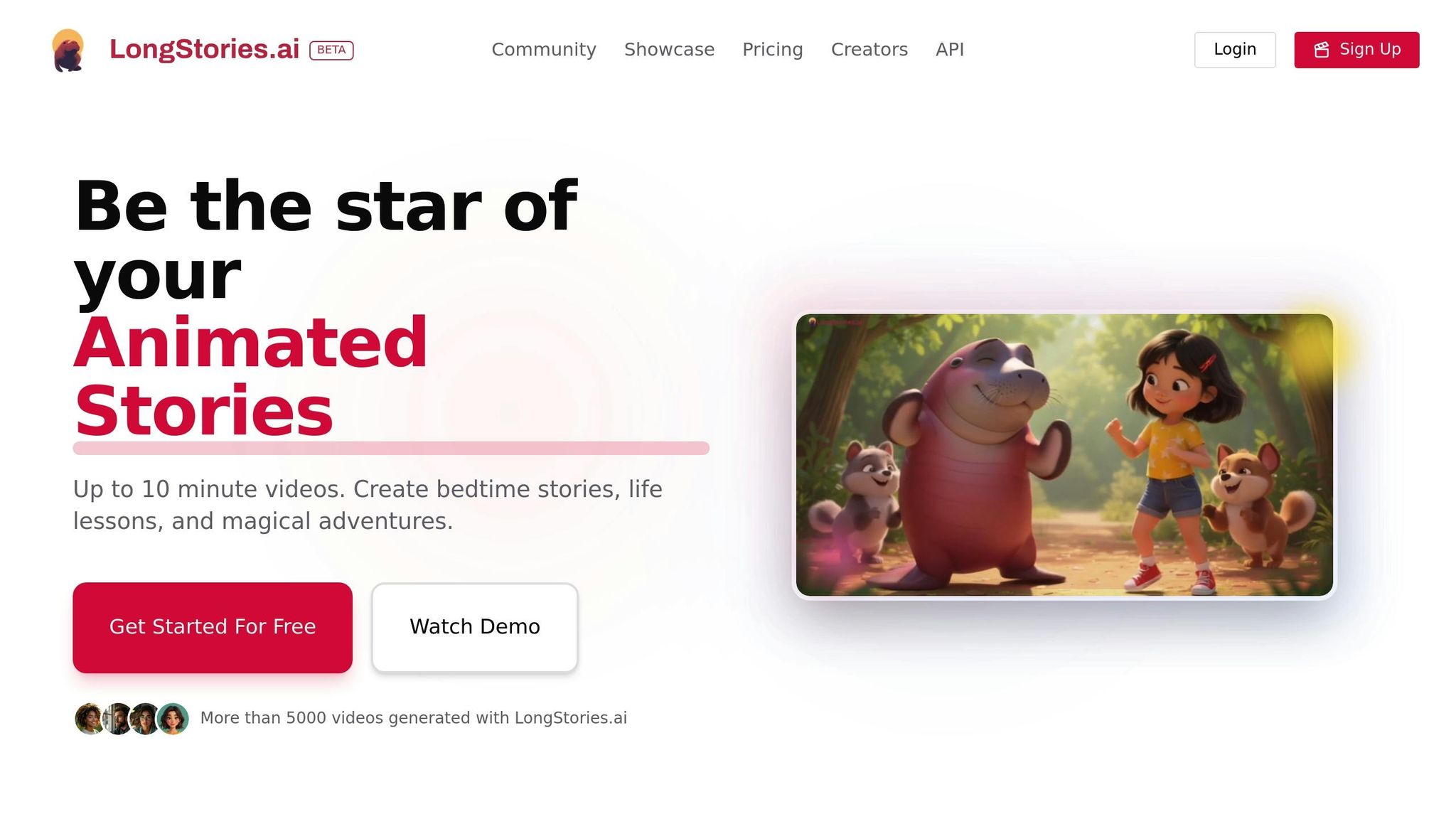
LongStories.ai showcases how AI can revolutionize multilingual, personalized storytelling. This platform bridges the gap between diverse learning needs by crafting tailored narratives for children in multiple languages. It’s a shining example of how AI fits into the growing trend of personalized educational tools.
How LongStories.ai Personalizes Storytelling
LongStories.ai takes storytelling to a new level by adapting to a variety of linguistic and creative preferences. Using AI, it generates stories based on user prompts while carefully weaving together character development, plot structure, and world-building. The platform draws from various storytelling frameworks to create unique narratives. Parents and educators can customize key elements such as characters, settings, themes, and the language of the story. The AI then tailors its output, adjusting word choices, grammar, and idioms to suit the chosen language seamlessly.
What sets LongStories.ai apart is its simplicity. With just one sentence, users can create a fully animated episode in under a minute. This ease of use has led to the creation of over 5,000 video adventures, featuring beloved AI characters like Manny the Manatee, Carter the Job Reporter, and Professor Time. By combining creativity with personalization, the platform not only entertains but also delivers meaningful educational benefits.
Educational Benefits of LongStories.ai
Personalized storytelling has a proven track record of enhancing literacy and creativity, helping children develop both language skills and emotional intelligence. Kids exposed to such tailored content often pick up new vocabulary faster than those reading traditional books.
The platform’s multilingual capabilities make it especially valuable in bilingual or multicultural environments. Studies highlight how AI storytelling tools can improve vocabulary, comprehension, and narrative skills while supporting cognitive and emotional growth. Furthermore, these tools offer a safe space for children to explore and process emotions.
LongStories.ai also embraces diversity and inclusion by incorporating global cultures, histories, and traditions into its narratives. This approach enables the platform to create richer, more meaningful content that resonates with children from different backgrounds.
Transforming Passive Entertainment into Active Learning
LongStories.ai turns screen time into an interactive learning experience, addressing concerns many parents have about digital media. Research shows that co-engagement - when children and caregivers explore digital content together - enhances learning, language development, and social skills. The platform supports this by creating shareable HD videos that families can watch and discuss, fostering deeper connections and understanding.
The AI narrators make complex topics approachable and engaging, while parents can extend the learning experience by encouraging offline activities like drawing or reenacting scenes from the stories. This approach shifts children from being passive viewers to active participants in their learning journey.
The platform’s instant content creation also makes it a practical tool for educators and parents alike, whether for classroom activities or bedtime stories that reinforce daily lessons. By delivering content that is both personal and culturally rich, LongStories.ai exemplifies how AI can transform education into a more inclusive and engaging experience.
Conclusion
AI-powered multilingual storytelling is reshaping the way we approach language learning and understanding diverse cultures. By creating tailored, contextually rich educational experiences, these technologies cater to individual learning styles and preferences, offering a more engaging and effective way to learn. This conclusion ties together insights from earlier discussions on language development, cultural significance, and the scalability of these systems.
Key Takeaways
AI storytelling tools are proving to be powerful in supporting early language development through features like interactivity, tailored content, and flexibility. These tools not only improve language and cognitive skills but also encourage emotional growth.
Advanced AI platforms meet critical educational challenges by offering seamless language transitions, real-time translations, and proficiency-based content customization.
The cultural depth of AI-generated content allows children to connect with their roots while acquiring new language skills. This is especially valuable for families with limited English proficiency, who may find traditional educational resources less accessible.
A standout example is LongStories.ai, a platform that has already created over 5,000 personalized video adventures. In less than a minute, it produces fully animated, culturally aware content, making multilingual education more accessible for both families and educators.
These developments highlight the transformative role AI can play in education, laying the groundwork for future innovations.
Future of AI in Educational Storytelling
Looking ahead, the potential of AI in storytelling and education is immense. As adaptive learning systems evolve, they are likely to offer personalized learning plans, AI-driven tutoring, and predictive analytics to address engagement challenges.
However, achieving this vision requires overcoming certain hurdles. Teachers will need thorough training to effectively integrate AI into classrooms. Additionally, addressing issues like equitable access and improving the technical capabilities of natural language processing systems will be crucial.
Above all, the future of AI in education depends on maintaining a balance between technology and the human touch. While AI can enhance learning experiences, it should complement rather than replace the empathy and emotional intelligence that human educators bring to the table.
The possibilities are undeniable - AI-driven multilingual storytelling has the power to revolutionize language learning and cultural understanding, paving the way for more inclusive, engaging, and effective educational opportunities worldwide.
FAQs
How does AI-driven storytelling help multilingual children improve their vocabulary and thinking skills?
AI-powered storytelling helps multilingual children by crafting customized and captivating stories that provide rich language-learning opportunities. These stories weave new vocabulary into the narrative, making it easier for kids to grasp and retain words through context.
What’s more, the interactive format of AI storytelling gets kids actively involved, which can sharpen their critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. By offering stories in various languages, it also strengthens their ability to transition between languages, improving their overall mental flexibility.
What challenges do AI storytelling platforms face in supporting less common languages, and how are they being addressed?
AI storytelling platforms encounter several hurdles when it comes to supporting less widely spoken languages. These challenges include a shortage of high-quality linguistic data, biases embedded in language models, and the difficulty of reflecting cultural subtleties accurately.
To tackle these problems, developers are focusing on reducing biases, designing specialized evaluation tools, and digitizing rare languages to create richer datasets. They’re also working to improve AI’s capability to comprehend and generate content in underrepresented languages, aiming to make storytelling more inclusive and accessible for a broader range of audiences.
How do AI storytelling tools create culturally sensitive and authentic stories?
AI storytelling tools achieve a deeper connection with diverse audiences by drawing from a wide range of datasets that include stories from various communities and traditions. This approach helps craft narratives that embrace different values and perspectives, making them relatable to children from all walks of life.
On top of that, human oversight is essential in fine-tuning these stories. Experts ensure the content respects cultural nuances and steers clear of harmful stereotypes. By blending AI's ability to process vast amounts of information with the careful guidance of human expertise, these tools can create stories that resonate across cultures and feel meaningful to everyone.
Related posts
LongStories is constantly evolving as it finds its product-market fit. Features, pricing, and offerings are continuously being refined and updated. The information in this blog post reflects our understanding at the time of writing. Please always check LongStories.ai for the latest information about our products, features, and pricing, or contact us directly for the most current details.